Enhancing Diagnostic Precision and Treatment Planning with CBCT
Accurate Diagnosis of Complex Root Anatomy
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) has transformed how endodontists visualize and understand root canal systems. Unlike traditional 2D X-rays that flatten complex structures into a single plane, CBCT creates detailed three-dimensional images that reveal the tooth's true internal architecture.
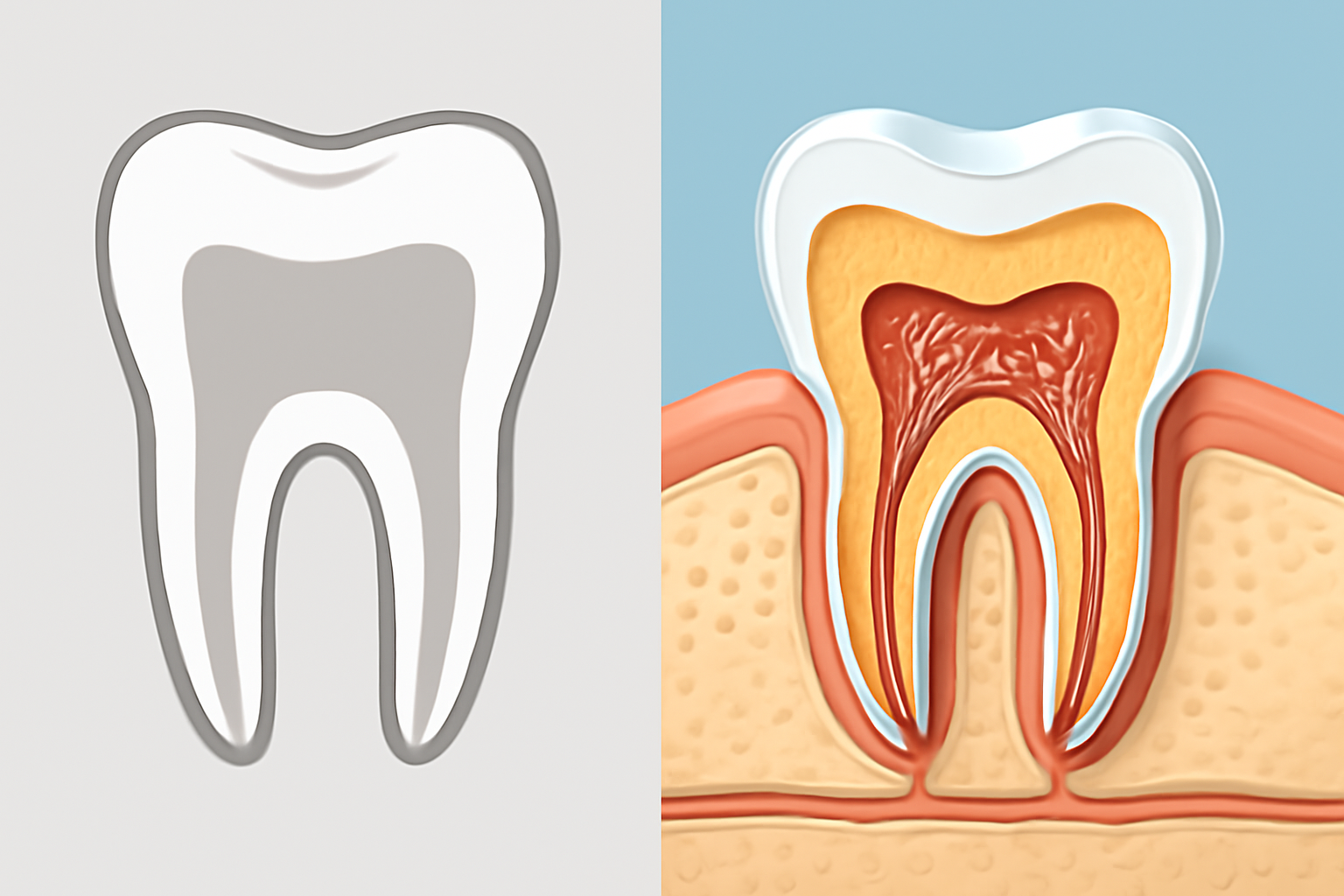 This advanced imaging shows the exact number of canals present, their precise locations, and any calcifications that might block access during treatment.
This advanced imaging shows the exact number of canals present, their precise locations, and any calcifications that might block access during treatment.
The human tooth can be surprisingly complex. For instance, a lower molar typically has three canals, but many patients have four or even five. Missing any of these canals during treatment almost guarantees failure. CBCT scans highlight these variations clearly, dramatically reducing the risk of missed canals that often lead to persistent infection and pain after seemingly successful procedures.
Root canals rarely run straight through teeth. They bend, curve, split, and sometimes form complex networks. CBCT imaging maps these intricacies before treatment begins, allowing endodontists to plan their approach. Knowing exactly where a canal curves sharply or divides into two branches helps prevent instrument breakage and perforation of the root structure.
Comprehensive Assessment of Periapical Health
The area surrounding the tooth root tip (periapical region) often harbors infection that's invisible to the naked eye. CBCT provides crystal-clear images of this critical area, revealing periapical lesions and bone changes that may be missed on standard X-rays. In fact, studies show CBCT can detect periapical lesions up to 27% more accurately than traditional radiographs.
This imaging technology detects bone changes and infection patterns much earlier than 2D X-rays. What might appear as a small shadow on a conventional X-ray often reveals itself as a significant lesion on CBCT. This early warning system allows for prompt intervention before extensive bone loss occurs, preserving more of the natural tooth structure and supporting bone.
Early Detection of Fractures and Traumatic Injuries
Tooth fractures present one of the most challenging diagnostic puzzles in dentistry. Tiny cracks and vertical root fractures often remain invisible on 2D images but can be visualized with CBCT's multidimensional capabilities. By catching these fractures early, endodontists can make informed decisions about whether to proceed with root canal treatment or recommend extraction if the fracture is too extensive.
Following dental trauma, CBCT proves invaluable for assessing damage beyond what's visible clinically. The technology excels at showing root fractures, luxations (tooth displacements), and alveolar bone fractures in remarkable detail. This comprehensive view helps clinicians develop appropriate treatment plans and provide more accurate prognoses.
Strategic Planning for Endodontic Procedures
CBCT's precise measurements and enhanced visibility transform treatment planning into a more predictable process. Endodontists gain confidence knowing exactly how deep to drill, which angle to approach from, and what obstacles might lie in their path. This clarity speeds up procedures while improving safety.
During treatment, CBCT helps clinicians avoid damaging critical anatomical structures. The technology clearly displays the mandibular nerve canal, maxillary sinus floor, and neighboring teeth roots – all vital structures that must remain undisturbed during endodontic procedures.
For surgical interventions like apicoectomies (root-end surgeries), CBCT provides surgical maps that guide the endodontist to the exact location of the root tip, showing its relationship to surrounding structures. This precision reduces tissue damage, shortens surgical time, and improves post-operative healing.
